Understanding eMMC Storage: What You Need to Know
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics and data storage, one term that frequently appears is eMMC storage. This compact, cost-effective storage solution is commonly used in smartphones, tablets, entry-level laptops, and various embedded systems. While it may not offer the blazing performance of SSDs, it fulfills essential data handling needs for lightweight applications. Understanding how eMMC storage functions and where it fits within today’s tech landscape can help consumers and tech enthusiasts make more informed decisions.
What is eMMC Storage?
Table of Contents
eMMC stands for embedded MultiMediaCard. It is a type of flash storage that is soldered directly onto a device’s motherboard, combining a controller and NAND flash memory in a single integrated unit. Unlike traditional storage, it is non-removable, which means users cannot upgrade or replace it easily.
eMMC is often used where a balance between performance, size, and cost is crucial. Although not as fast or as robust as SSDs, eMMC still provides solid performance for tasks such as web browsing, media consumption, and document management.
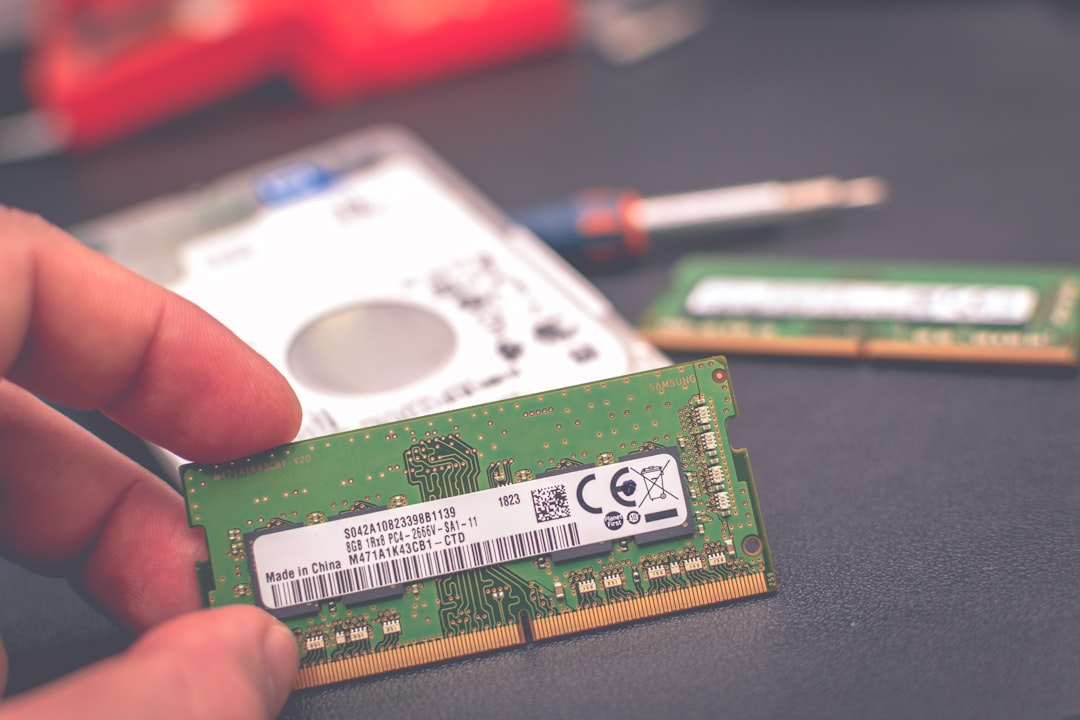

Key Advantages of eMMC Storage
- Cost-Effective: One of the most significant benefits of eMMC is its affordability. For budget devices, this storage option helps keep prices low.
- Low Power Consumption: Because it’s tailored for less demanding tasks, eMMC consumes relatively less power, which contributes to longer battery life in mobile devices.
- Simplicity of Integration: Manufacturers favor eMMC for its ease of integration into compact devices, helping streamline the development process and reduce overall device size.
Limitations of eMMC
Despite its benefits, eMMC is not without its drawbacks. For one, its performance lags behind that of SSDs in both read/write speed and data durability. This can affect multitasking, app launching, and file transfers in more robust systems. Additionally, due to its soldered nature, any failure in the storage means the whole motherboard may need replacement—something not ideal for consumer repairs.

eMMC Storage vs. SSD: What’s the Difference?
While both SSDs and eMMC serve as solid-state storage solutions, they differ in terms of structure, speed, and intended usage. SSDs use higher-quality NAND memory and more advanced controllers, offering faster access times and better durability. They are typically found in mid-range to high-end computers and can handle intensive tasks such as gaming, video editing, and running multiple heavy applications.
eMMC, on the other hand, is geared toward devices that require minimal storage performance. It shines in affordability and is primarily found in budget phones, tablets, Chromebooks, and smart appliances.
Common Use Cases for eMMC Storage
- Entry-Level Smartphones: These phones focus on affordability and general usability, where eMMC is sufficient.
- Tablets and E-Readers: Devices that primarily serve media consumption benefit from the compact nature of eMMC.
- Budget Laptops and Chromebooks: For performing light computing tasks, eMMC provides a reliable storage option.
- Embedded Systems: IoT gadgets and smart home devices leverage eMMC for seamless integration and low energy use.
Future Outlook
With UFS (Universal Flash Storage) and NVMe-based SSDs gaining popularity, especially in smartphones and laptops, the future of eMMC appears limited to low-budget and embedded applications. Nevertheless, its role remains crucial in minimizing cost while delivering essential storage functionality.
FAQ: Understanding eMMC Storage
-
Q: Can I upgrade eMMC storage?
A: Unfortunately, no. eMMC is soldered onto the motherboard, making it non-upgradable. -
Q: Is eMMC better than HDD?
A: For read/write speed and power efficiency, eMMC usually outperforms HDD in smaller devices, but HDD still offers more storage capacity at a lower cost. -
Q: How long does eMMC storage last?
A: The lifespan of eMMC depends on usage, but typically, it can last between 3 to 5 years under regular conditions. -
Q: Are apps slower on eMMC-based devices?
A: Yes, you may notice slower load times or lag in comparison to SSD-based devices, especially with demanding apps. -
Q: Can I use eMMC for gaming?
A: eMMC is not ideal for gaming due to its slower data transfer rates and limited capacity. SSDs are recommended for gaming devices.